🚀 Intersection Point Of Y Shaped Linked List
- Before moving on to the solution part, try this question Problem link .
Statement :
- Given two singly linked lists of size N and M, write a program to get the point where two linked lists intersect each other.
Example :
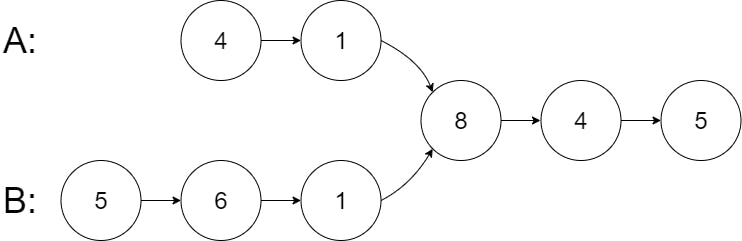
Input:
- A =
4->1->8->4->5->NULL - B =
5->6->1->8->4->5->NULL
Output:
8
Explanation :
Your Task:
- Your task is to write code to get the intersection of these two linked lists.
Challenge:
try to solve the question without using any extra space
- Expected Time Complexity :
O(N+M) - Expected Auxiliary Space :
O(1)
Constraints:
1 ≤ N + M ≤ 2*105-1000 ≤ value ≤ 1000
Solution
🚀 Method - 1 :
Logic :
- Create a empty Hash table to store every node in linked list.
- Traverse the first list and store every node into hash table.
- Traverse the second list and check if current node is present in hash table or not.
- if(present) :
return curr->data - else :
curr=curr->next
- if(present) :
Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = NULL;
prev = NULL;
}
};
Node *insert(Node *ptr, int v)
{
Node *temp = new Node(v);
if (ptr == NULL)
{
return temp;
}
Node *head = ptr;
while (head->next != NULL)
{
head = head->next;
}
head->next = temp;
return ptr;
}
Node *intersectPoint(Node *a, Node *b)
{
unordered_set<int> hash;
// storing data of 1st node into hash table
Node *temp = a;
while (temp != NULL)
{
hash.insert(temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
// trversing 2nd list
Node *curr = b;
while (curr != NULL)
{
if (hash.find(curr->data)!=hash.end())
{
return curr;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
Node *head1 = NULL;
int n1;
cout << "Enter the size of 1st linked list : ";
cin >> n1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n1; i++)
{
int c;
cin >> c;
head1 = insert(head1, c);
}
Node *head2 = NULL;
int n2;
cout << "Enter the size of 1st linked list : ";
cin >> n2;
for (int i = 1; i <= n2; i++)
{
int c;
cin >> c;
head2 = insert(head2, c);
}
if (intersectPoint(head1, head2) == NULL)
{
cout << "Linked lists do not have any intersection point." << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Linked lists are intersected at Node " << intersectPoint(head1, head2)->data << endl;
}
return 0;
}
🚀 Method - 2 :
Logic :
- First find
Len1( Length of 1st linked list ) andLen2( Length of 2nd linked list ). - Then traverse the bigger linked list for
abs(len1 - len2)times. - After traversing for
abs(len1-len2)times bigger list and smaller list now have same number of nodes. - Now traverses both list
- if we find any common node then return that node.
- else after loop termination return NULL.
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = NULL;
prev = NULL;
}
};
Node *insert(Node *ptr, int v)
{
Node *temp = new Node(v);
if (ptr == NULL)
{
return temp;
}
Node *head = ptr;
while (head->next != NULL)
{
head = head->next;
}
head->next = temp;
return ptr;
}
Node *intersectPoint(Node *a, Node *b)
{
int c1 = 0;
int c2 = 0;
Node *curr1 = head1;
Node *curr2 = head2;
while (curr1 != NULL)
{
curr1 = curr1->next;
c1++;
}
while (curr2 != NULL)
{
curr2 = curr2->next;
c2++;
}
int v = abs(c1 - c2);
Node *temp1 = (c1 > c2) ? head1 : head2;
Node *temp2 = (c1 > c2) ? head2 : head1;
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++)
{
temp1 = temp1->next;
}
while (temp1 != NULL and temp2 != NULL)
{
if (temp1 == temp2)
{
return temp1;
}
temp1 = temp1->next;
temp2 = temp2->next;
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
Node *head1 = NULL;
int n1;
cout << "Enter the size of 1st linked list : ";
cin >> n1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n1; i++)
{
int c;
cin >> c;
head1 = insert(head1, c);
}
Node *head2 = NULL;
int n2;
cout << "Enter the size of 1st linked list : ";
cin >> n2;
for (int i = 1; i <= n2; i++)
{
int c;
cin >> c;
head2 = insert(head2, c);
}
if (intersectPoint(head1, head2) == NULL)
{
cout << "Linked lists do not have any intersection point." << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Linked lists are intersected at Node " << intersectPoint(head1, head2)->data << endl;
}
return 0;
}
🚀 Complexity Analysis
| Methods | Time | Space |
| 1. | O(N) | O(N) |
| 2. | O(N) | O(1) |
😇 Thanks for Visiting
😊 Connect With Me On Linkedln Linkedln Profile.